ЛЕКЦИЯ № 33. Pleura
ЛЕКЦИЯ № 33. Pleura
Visceral pleura is a thin serous membrane that covers the outer surface of the lungs. A delicate connective tissue layer of collagen and elastin, containing lymphatic channels, vessels, and nerves, supports the membrane. Its surface is covered by simple squamous mesotheli-um with microvilli.
Parietal pleura is that portion of the pleura that continues onto the inner aspect of the thoracic wall. It is continuous with the visceral pleura and is lined by the same mesothelium.
Pleural cavity is a very narrow fluid-filled space that contains mo-nocytes located between the two pleural membranes. It contains no gases and becomes a true cavity only in disease (e. g., in pleural infection, fluid and pus may accumulate in the pleural space). If the chest wall is punctured, air may enter the pleural space (pneumothorax), breaking the vacuum, and allowing the lung to recoil. Parietal pleura lines the inner surface of the thoracic cavity; visceral pleura follows the contours of the lung itself.
Pleural cavity: The pleural cavity is the space between the parietal and viscer al layers of the pleura. It is a sealed, blind space. The intro-duc tion of air into the pleural cavity may cause the lung to col lapse (pneumothorax).
It normally contains a small amount of serous fluid elaborated by mesothelial cells of the pleural membrane.
Pleural reflections are areas where the pleura changes direction from one wall to the other. The sternal line of reflection is where the costal pleura is con tinuous with the mediastinal pleura behind the sternum (from costal cartilages 2-4). The pleural margin then passes in-feriorly to the level of the sixth costal cartilage. The costal line of reflection is where the costal pleura becomes continuous with the diaphragmatic pleura from rib 8 in the midclavicular line, to rib 10 in the midaxillary line, and to rib 12 lateral to the vertebral column. Pleural recesses are potential spaces not occupied by lung tissue except during deep inspiration. Costodiaphragmatic recesses are spaces below the inferior borders of the lungs where costal and diaphragmatic pleura are in contact. Costomediastinal recess is a space where the left costal and mediastinal parietal pleura meet, leaving a space due to the cardiac notch of the left lung. This space is occupied by the lingula of the left lung during inspiration.
In nervation of the parietal pleura: The costal and peripheral portions of the diaphragmatic pleu ra are supplied by intercostal nerves.
The central portion of the diaphragmatic pleura and the medi asti-nal pleura are supplied by the phrenic nerve.
New words
visceral – висцеральный
pleura – плевра
delicate – тонкий
collagen – коллаген
elastin – эластин
containing – содержание
lymphatic channels – лимфатические сосуды
nerves – нервы
to support – поддерживать
covered – покрытый
squamous – чешуйчатый
microvilli – микроворсинки
parietal pleura – париетальная плевра
onto aspect – в аспекте
visceral pleura – висцеральная плевра
inspiration – вдохновение
costal – реберный
Степени сравнения прилагательных Таблица 4.
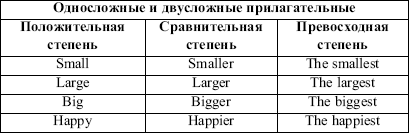
Особые случаи образования степеней сравнения Таблица 5.

Образуйте сравнительную и превосходную степень следующих прилагательных. Не забудьте употреблять определенный артикль перед превосходной степенью прилагательных.
Hot, long, short, clever, silly, great, red, black, white, thin, thick, fat, nice, warm, cold, merry small, tall, high, weak, strong, heavy, light, green, dry, clean, dirty, wide, deep, brave.
Переведите на английский язык.
Старый, старше, самый старый, самый старший, мой старший брат, мой старый друг, дальше, самый дальний, самый длинный, короче, счастливый, счастливее, самый счастливый, самый лучший, самый черный, длиннее, хуже, лучше, теплее, ее лучший друг, ее младший сын, его старший сын.
Answer the questions.
1. What is visceral pleura?
2. Is visceral pleura a thin serous membrane or not?
3. What contains lymphatic channels, vessels, and nerves?
4. What covers delicate connective tissue layer?
5. Which portion of the pleura is parietal pleura?
6. What kind of space is pleural cavity?
7. What do pleural cavity contain?
8. In which way air may enter the pleural space?
9. What do normally contain a small amount of serous fluid?
10. What is supplied by intercostal nerves?
Make the sentences of your own using the new words (10 sentences).
Find the verb to be in the text. Explain why it is used in such a way?
Более 800 000 книг и аудиокниг! 📚
Получи 2 месяца Литрес Подписки в подарок и наслаждайся неограниченным чтением
ПОЛУЧИТЬ ПОДАРОКЧитайте также
25-я ЛЕКЦИЯ
25-я ЛЕКЦИЯ Sanguinaria и Chelidonium Прежде чем приступить к изучению Sanguinaria я хочу сказать вам, что есть разновидность мака, растущая в Мексике и называемая Argemone Mexicana. Это растение употребляется в Мексике совершенно таким же образом, как у нас Opium. Оно вызывает также кожные сыпи и
26-я ЛЕКЦИЯ
26-я ЛЕКЦИЯ Cucurbitaceae — Тыквенные Cucurbitaceae:1. Colocyinths cucumis.2. Bryonia alba3. Citrullus. Семена мочегонны.4. Cucurbita (скваш-s quash тыква).5. Momordica balsamum. Ветры.6. Flaterium momordica. Кишки и лихорадка.Сегодня мы начнем изучение Cucurbitaceae. Это семейство дает нам около шести или восьми лекарств, а также несколько
28-я ЛЕКЦИЯ
28-я ЛЕКЦИЯ Coniferae и Euphorbiaceae Coniferae — Хвойные Pinus sylvestris. Детская атрофия. Abies nigra. Желудок. Sabina Juniperus. Выкидыш.Terebenthina.1. Почки, мочевой пузырь и пр.2. Слизистые оболочки.3. Матка.4. Тифозные состояния.5. Почечная водянка.Сравните — Arsenicum, Cantharis, Copaiva, Camphora, Phosphorus.Pix liquida. Легкие
29-я ЛЕКЦИЯ
29-я ЛЕКЦИЯ Ranunculaceae — Лютиковые Aconitum.Helleborus niger.Paeonia.Pulsatilla.Hydrastis.Staphisagria.Actea racemosa.Actea spicata.Radix coptidis.Ranunculus
33-я ЛЕКЦИЯ
33-я ЛЕКЦИЯ Rubiaceae — Мареновые Rubiaceae:1. Rubia titctoiria (Марена).2. Galium (Тоже красная краска).3. Cinchona.4. Ipecacuanha.5. Coffea.6. Mitchella.7. Gambier.Сегодня перед нами семейство растений, из которого мы получаем три очень ценных средства, Cinchona, Ipecacuanha и Coffea. Это семейство дает нам также Gambier (Gambogia,
35-я ЛЕКЦИЯ
35-я ЛЕКЦИЯ Scrophulariaceae — Норичниковые China. Из этого семейства растений мы получаем Digitalis, Gratiola, Leptandra viginica, Euphrasia, Verbascum и Linaria. У нас имеется немного симптомов для каждого из этих средств, и те, которые известны, достаточно определенны, чтобы их легко запомнить. Важнейшим
37-я ЛЕКЦИЯ
37-я ЛЕКЦИЯ Solanaceae — Пасленовые Solanaceae:1. Belladonna.2. Hyoscyamus.3. Stramonium.4. Solan um nigr.5. Tabacum.6. Dulcamara.7. Capsicum.Средства, образующие эту группу по своей симптоматологии очень сходны друг с другом. Едва ли найдется хоть один симптом у этих средств, который не встречался бы почти в том же виде
42-я ЛЕКЦИЯ
42-я ЛЕКЦИЯ Минеральная группа В прилагаемой таблице я разместил для вашего изучения элементы по их взаимному соотношению до некоторой степени так же, как мы находим это в химии. Поэтому они не расположены в порядке, принятом в фармакологии. Но ведь это не абсолютный
44-я ЛЕКЦИЯ
44-я ЛЕКЦИЯ Угольная группа 1. Carbo animalis (содержит фосфат извести).2. Carbo vegetabilis (содержит углекислое кали).3. Graphites (содержит железо).4. Anilin-sulphat.5. Carboneum (сажа).6. Угольный газ.7. Бисульфид угля (сероуглерод).Сегодня я займу ваше внимание лекарствами, получаемыми из угольной
63-я ЛЕКЦИЯ
63-я ЛЕКЦИЯ Соли извести (Calcarea) Существует целый ряд солей извести, более или менее хорошо исследованных. Первая на этой таблице стоит Calcarea ostrearum или устричная известь. Этот препарат, данный нам Ганеманом, был испытан в качестве углекислой соли извести, Calcarea carbonica. Его
65-я ЛЕКЦИЯ
65-я ЛЕКЦИЯ Препараты натрия Препараты Соды (Натрия) в химическом и медицинском отношении совершенно сходны с препаратами Поташа (Калия), но это сходство не таково, чтобы они не могли быть назначаемы вслед за солями Калия. Мы увидим, что Kali carb. служит дополнением для Natrum mur. в
68-я ЛЕКЦИЯ
68-я ЛЕКЦИЯ Соли Калия Токсикологически калий может представлять для вас некоторый интерес, когда кто-либо случайно проглотит едкое кали. Большое сродство этого вещества к воде заставляет его жадно отнимать воду от тканей и в результате получается глубокий ожег
38. Pleura
38. Pleura Visceral pleura is a thin serous membrane that covers the outer surface of the lungs. A delicate connective tissue layer of collagen and elastin, containing lymphatic channels, vessels, and nerves, supports the membrane. Its surface is covered by simple squamous mesothelium with microvilli.Parietal pleura is that portion of the pleura that continues onto the inner aspect of the thoracic wall. It is continuous with the visceral pleura and is lined by the same me—sothelium.Pleural
Лекция № 9. Шок
Лекция № 9. Шок Шок – это форма критического состояния организма, проявляющаяся множественной органной дисфункцией, каскадно развивающейся на основе генерализованного кризиса циркуляции и, как правило, заканчивающаяся летально без лечения.Шоковый фактор – это любое
ЛЕКЦИЯ № 1. Вводная лекция. Медицинская символика различных времен и народов
ЛЕКЦИЯ № 1. Вводная лекция. Медицинская символика различных времен и народов История медицины – это наука о развитии, совершенствовании медицинских знаний, медицинской деятельности разных народов мира на протяжении всей истории человечества, которая находится в
Лекция 1
Лекция 1 Еще раз здравствуйте, уважаемые соратники.Начинаем наше первое занятие в Народном университете здорового образа жизни по методу Геннадия Андреевича Шичко. Курс будет посвящен коррекции зрения по методу Шичко-Бейтса. Это курс общего оздоровления и избавления от